Chicky Run Juego: ¡Corre, Salta Y Diviértete En Esta Emocionante Aventura!
Revisión de Chicky Run de PG Soft
Chicky Run es una emocionante aventura que ofrece una experiencia de juego única y entretenida. Desarrollada por PG Soft, esta tragamonedas destaca por su diseño colorido y dinámico, que atrae a los jugadores desde el primer momento. La mecánica de juego es intuitiva, lo que la convierte en una opción perfecta tanto para jugadores novatos como para aquellos con más experiencia. Además, la posibilidad de probar la demo versión permite a los usuarios familiarizarse con el juego antes de realizar apuestas reales.
La gran variedad de características especiales, como giros gratis y bonificaciones, hace que Chicky Run sea aún más atractiva. La calidad de los gráficos y los efectos de sonido suman a la experiencia inmersiva, creando un ambiente divertido y cautivador. Si deseas disfrutar de esta emocionante tragamonedas, puedes descargar la versión APK en tu dispositivo móvil, lo que te permitirá jugar en cualquier lugar y en cualquier momento.
| 🎮 Nombre del juego | Chicky Run |
| 📅 Fecha de lanzamiento | 2023 |
| 🎨 Proveedor | PG Soft |
| 💰 RTP | 96.75% |
| 🎲 Volatilidad | Media |
| 🏆 Líneas de pago | 20 |
| 🌟 Símbolos especiales | Símbolos Wild y Scatter |
| 🆓 Giros gratis | Sí |
| 📱 Móvil | Compatible |
| 💻 Plataforma | 5 |
| 🛠️ Bonus | Bonificación de re-spin |
| 📊 Apuestas mínimas | 0.20 |
| 📈 Apuestas máximas | 100.00 |
| 🗺️ Idiomas disponibles | Multilenguaje |
| 💾 Demos | Disponibles |
Versión móvil de Chicky Run
La versión móvil de Chicky Run ofrece la misma calidad y emoción que su contraparte de escritorio. Los jugadores pueden disfrutar de gráficos vibrantes y una jugabilidad fluida directamente desde sus dispositivos móviles. Para aquellos que prefieren jugar sobre la marcha, simplemente es necesario descargar el archivo APK correspondiente. Esto permite acceder a la tragamonedas en cualquier lugar, sin necesidad de conexión a un ordenador.
La optimización para dispositivos móviles asegura que todas las características del juego, incluyendo giros gratis y bonos, estén disponibles en la palma de tu mano. Además, la jugabilidad es intuitiva, lo que garantiza que incluso los nuevos jugadores puedan fácilmente navegar por la interfaz y disfrutar de la experiencia. Descargar Chicky Run en formato APK es un proceso sencillo y rápido.
Pros y Contras
Pros
- Gráficos atractivos y vibrantes
- Posibilidad de jugar en versión demo
- Bonificaciones emocionantes y giros gratis
- Compatible con dispositivos móviles
- Facilita el juego intuitivo para todos los niveles
Contras
- No todos los casinos en línea ofrecen esta tragamonedas
- Algunas funciones pueden no estar disponibles en la demo
- Requiere descarga para jugar en móvil
- La volatilidad media puede no ser del agrado de todos
- Dependencia de la conexión a Internet para algunas funciones
PG Soft: Desarrollador de Chicky Run
PG Soft (Pocket Games Soft) es un reconocido desarrollador de juegos de casino que lanzó Chicky Run en septiembre de 2023. Esta empresa se ha destacado en la industria por crear títulos con gráficos impresionantes y mecánicas de juego innovadoras. El arte suministrado por PGSoft en Chicky Run es increíble, con un tono y estilo muy animado que atrae a los jugadores. La simplicidad del juego, combinada con características únicas como el sistema de carriles y multiplicadores progresivos, demuestra la capacidad de PG Soft para crear experiencias de juego entretenidas y accesibles.
Bonos y Free Spins en Chicky Run
Característica principal de bonificación
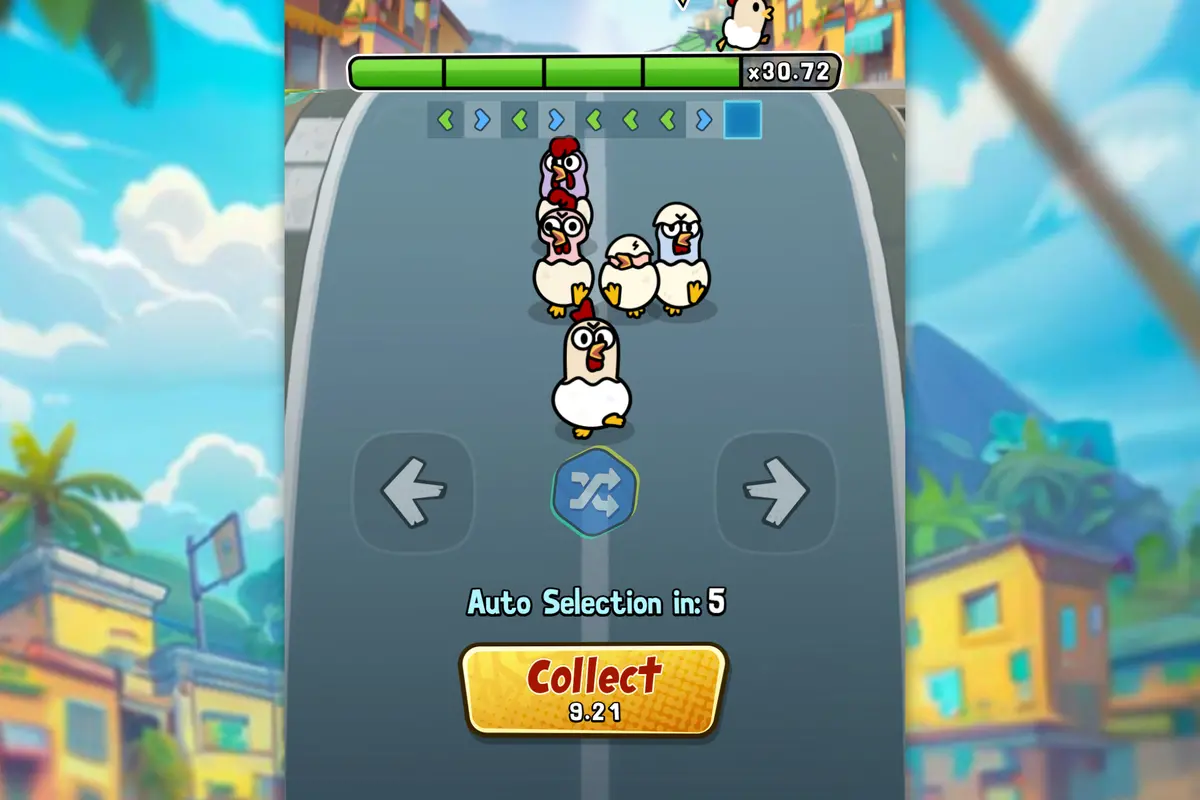
La característica principal de Chicky Run es el multiplicador de ganancias que puede aumentar el potencial de pago. Los jugadores pueden obtener los siguientes multiplicadores:
- Primera victoria = 1,92x la apuesta total
- Segunda victoria consecutiva = 3,84x la apuesta total
- Tercera victoria = 7,68x la apuesta total
- Cuarta victoria = 15,36x la apuesta total
- Quinta victoria consecutiva = 30,72x la apuesta total
Free Spins en Chicky Run
La función de Giros Gratis se activa cuando aparecen tres o más símbolos Scatter en cualquier lugar de los rodillos. Los jugadores reciben inicialmente 10 giros gratis, con la posibilidad de ganar más durante la función. Durante los giros gratis, se aplica un multiplicador progresivo que aumenta con cada victoria consecutiva.
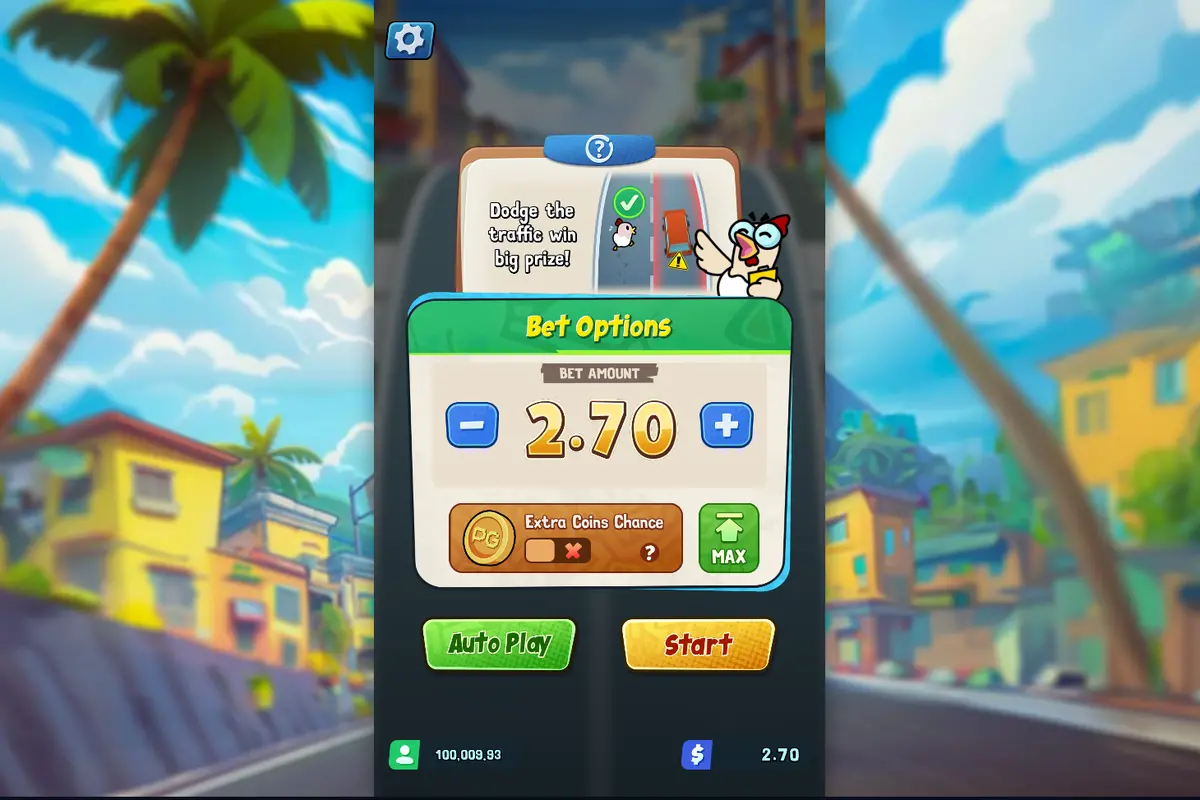
Extra Coins Chance
Otra característica especial es "Extra Coins Chance", que los jugadores pueden activar aumentando su apuesta en un 50%. En cualquier ronda ganadora, los jugadores pueden ganar 1, 2 o 3 monedas especiales. Estas monedas valen la mitad de la cantidad de la apuesta antes de que las apuestas incurran en un costo incrementado del 50%, lo que añade un elemento estratégico al juego.
Cómo registrarse y jugar Chicky Run con dinero real
Para jugar a Chicky Run con dinero real, primero debes registrarte en un casino online que ofrezca juegos de PG Soft. El proceso de registro generalmente requiere proporcionar información personal básica, crear un nombre de usuario y contraseña, y verificar tu cuenta mediante correo electrónico o teléfono. Una vez registrado, deberás realizar un depósito utilizando uno de los métodos de pago disponibles como tarjetas de crédito, billeteras electrónicas o transferencias bancarias. Los casinos suelen ofrecer bonos de bienvenida que puedes utilizar para aumentar tu bankroll inicial. Después de completar el depósito, simplemente busca Chicky Run en la sección de tragamonedas del casino, selecciona tu apuesta (desde €0,20 hasta €75) y comienza a jugar para experimentar la emocionante mecánica de carriles y multiplicadores progresivos que hacen único a este juego.
Preguntas frecuentes sobre Chicky Run de PG Soft
¿Qué es Chicky Run y en qué consiste?
Chicky Run es un juego de azar desarrollado por PG Soft, ambientado en las calles de Río de Janeiro. El objetivo principal es ayudar a un pollito a cruzar una carretera muy transitada, esquivando coches y otros obstáculos. Por cada cruzada exitosa, el multiplicador de ganancias aumenta y pueden unirse más pollitos a la carrera.
¿Cómo se juega una ronda en Chicky Run?
Antes de cada carrera, el jugador elige si comenzar por el lado izquierdo o derecho de la carretera, o puede usar una opción de botón aleatorio. Cada vez que el pollito cruza con éxito, el jugador puede decidir continuar o cobrar sus ganancias, evitando el riesgo de ser golpeado por un coche.
¿Qué función tiene el botón de recolección?
El botón de recolección permite al jugador cobrar sus ganancias acumuladas después de cada cruce exitoso. Si decides continuar y el pollito es atropellado, se pierden las ganancias de esa ronda.
¿Qué es la función de Oportunidad de Monedas Extra?
Esta función se puede activar y otorga la posibilidad de recibir entre una y tres monedas adicionales en cada ronda ganadora. Estas monedas tienen un valor de la mitad de la apuesta inicial, antes de aplicar el incremento del 50% por la función extra.
¿El gráfico de direcciones tiene alguna utilidad en el juego?
Sí, el gráfico bajo el medidor de multiplicador muestra las direcciones por donde no han pasado coches en las diez rondas anteriores, ayudando a los jugadores a planificar mejor su siguiente movimiento.
¿Puedo jugar a Chicky Run gratis?
Existen versiones demo de Chicky Run disponibles en varios casinos online, que permiten jugar sin apostar dinero real. Así puedes conocer las mecánicas antes de realizar apuestas con dinero.
¿Hay estrategias para aumentar las probabilidades de ganar en Chicky Run?
Si bien Chicky Run es un juego de azar y el resultado depende en gran medida de la suerte, observar las estadísticas de las últimas rondas y utilizar la opción de recolección en el momento adecuado puede ayudar a maximizar las ganancias y reducir las pérdidas.
